leehyeon-dv 님의 블로그
4.4 A Simple Implementation Scheme 본문
간단한 구현 개요
🔑Table of Contents
- ALU Control
- The Main Control Unit
- Datapath with Control
- R-type Instruction
- R-Type instuction의 Data 및 Control 흐름
- Load Instruction
- Load Instruction 의 Data 및 Control 흐름
- Branch-on-Equal Instruction
- Branch Instruction의 data 및 control흐름
- Implementing Jumps
- Datapath with jumps added
- Adding the Jump Operation
- Performance Issues
📌ALU Control
- ALU는 다음에 쓰임
- Load/Store : F = add (레지스터에저장된 값 +4를 읽어 계산한다)
- Branch: F = subtract
- R-type: F는 funct fidld에 따라 다르다
| ALU control | 기능 |
| 0000 | AND |
| 0001 | OR |
| 0010 | add |
| 0110 | subtract |
| 0111 | set-on-less-than(SLT) |
| 1100 | NOR |
| opcode | ALUOP | Operation | funct | ALUfunction | ALUcontrol |
| lw | 00 | load word | x | add | 0010 |
| sw | 00 | store word | x | add | 0010 |
| beq | 01 | branch equal | x | subtract | 0110 |
| R-type | 10 | add | 100000(32) | add | 0010 |
| subtract | 100010(34) | subtract | 0110 | ||
| AND | 100100(36) | AND | 0000 | ||
| OR | 100101(37) | OR | 0001 | ||
| set-on- less-than(SLT) |
101010(42) | set-on- less-than |
0111 |
📌THE Main control Unit
control신호는 명령어로 부터 얻어진다
| R-type | 0 | rs | rt | rd | shamt | funct |
| lw/sw | 35 | 43 | rs | rt | address | ||
| Branch | 4 | rs | rt | address | ||
📌Datapath with Control

📌 R-Type Instruction

📌 R-Type Instruction의 Data 및 control흐름
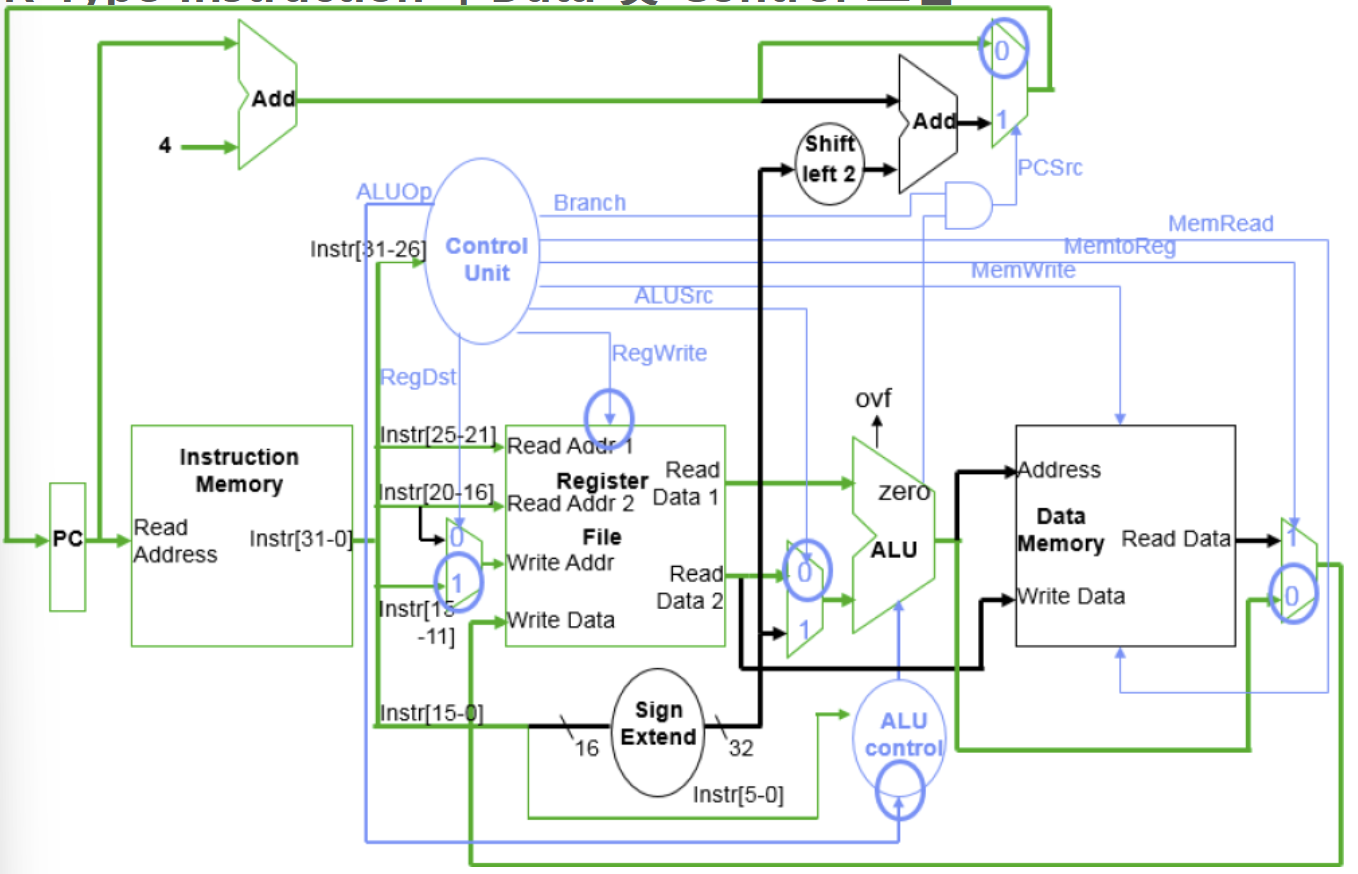
→ PC +4 계산 && PC →instruction Memory
→ control 유닛
예 (add)
| ALUOp | Branch | RegDst | MemRead | MemToReg | MemWrite | RegWrite | ALUSrc |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
- 예(addi)
| ALUOp | Branch | RegDst | MemRead | MemToReg | MemWrite | RegWrite | ALUSrc |
| 00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
- RegDst : 데이터를 쓰기전에 어떤 값이 저장될지 결정 ((1)r-type: rd레지스터, (0)i-type : rt)
- ALUOp : ALU가 수행할 연산 유형지정
- RegWrite : 레지스터 쓰기활성화 여부 결정
- ALUSrc : ALU에 입력으로 들어갈 값 결정(레지스터 값 or 상수)
→ register File
- Read register1 : rs에서 값 읽기
- Read register 2 : rt에서 값 읽기
→ ALU
- Read data1 : rs
- Read data2 : rt → MUX(0 : rt 레지스터값 선택/1: i-type 명령어)
- control unit에서 ALU Control에 따라 ALU가 지정된 연산 수행
→ Register
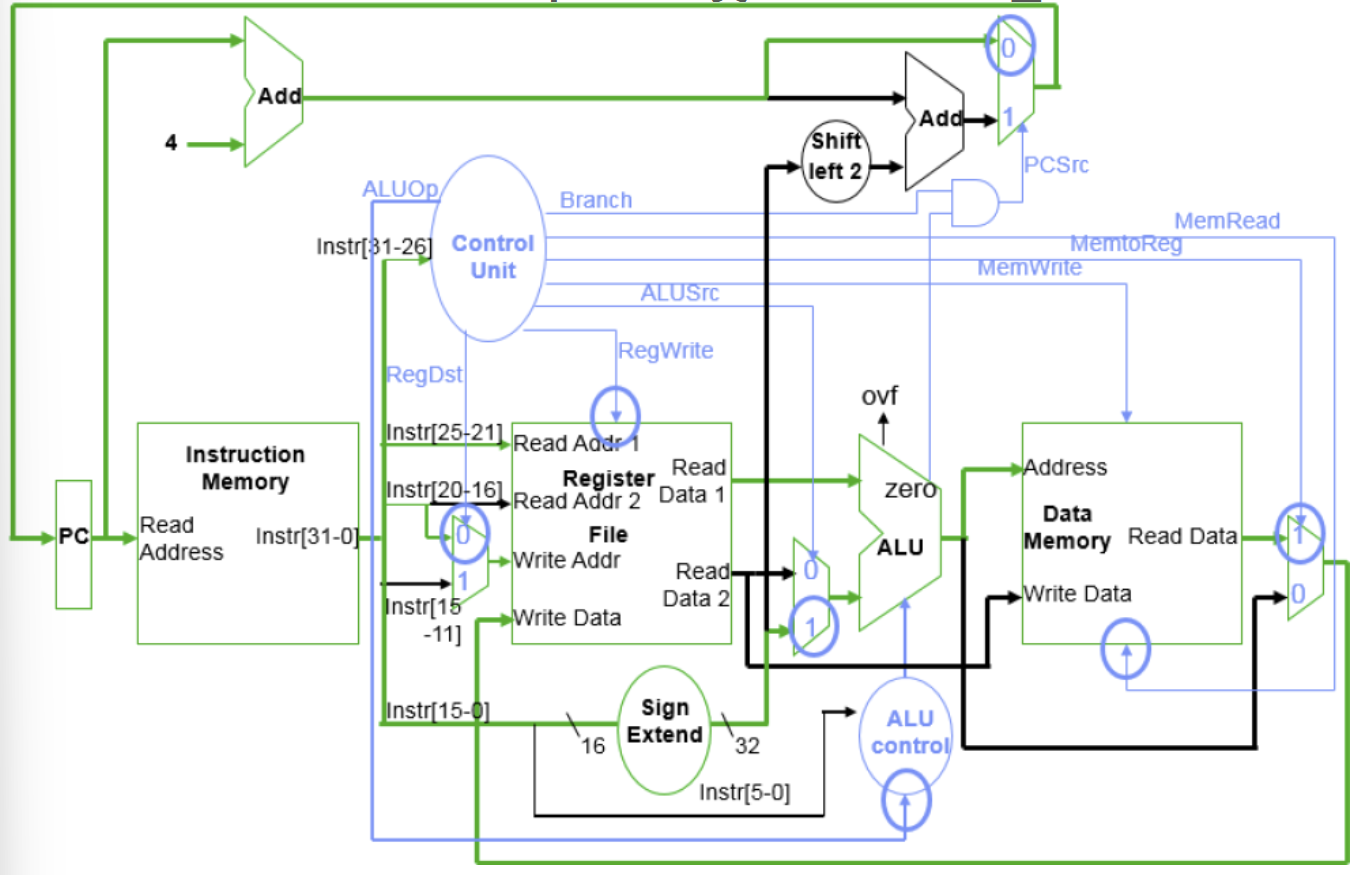
📌 Load Instruction
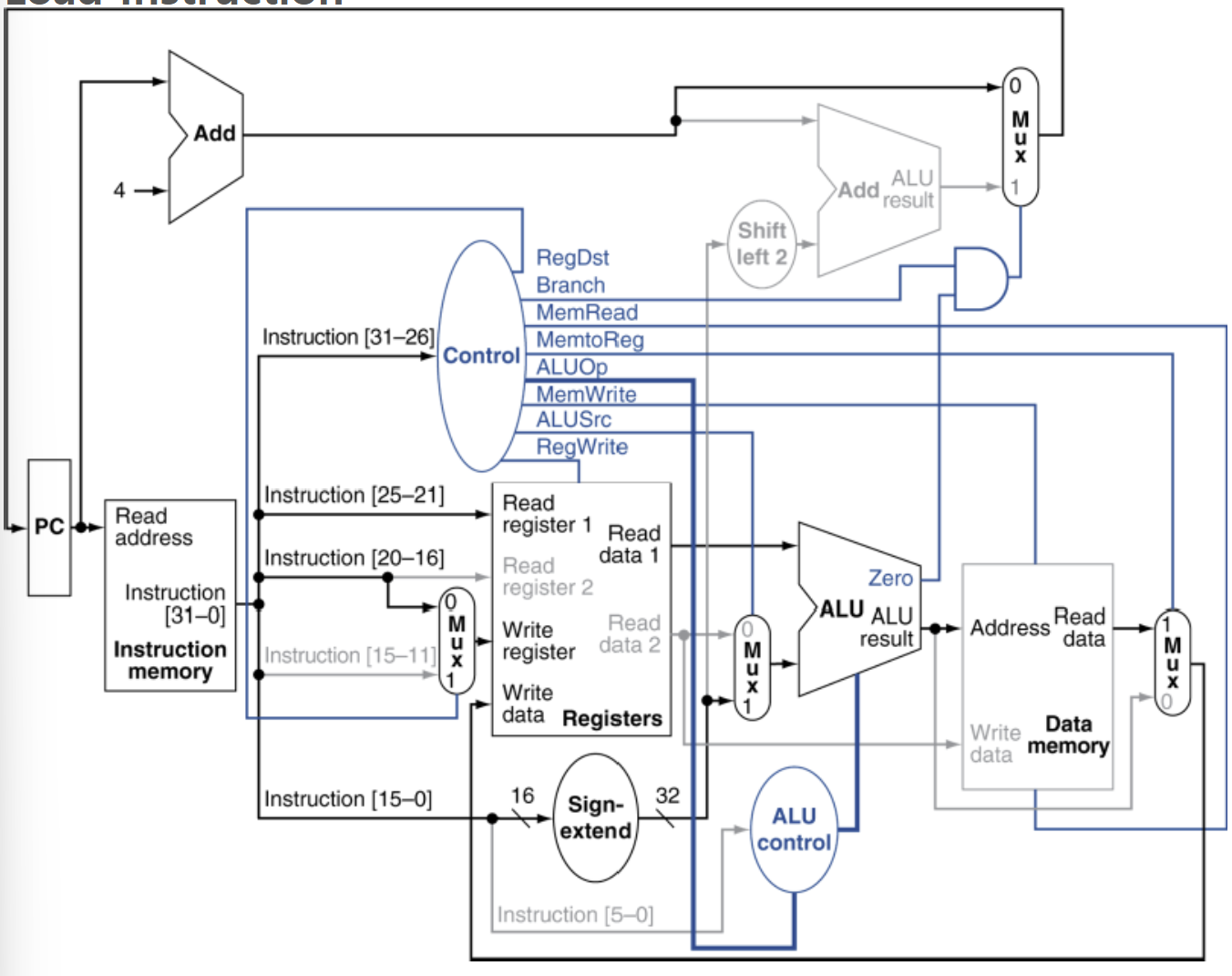
📌 Load word Instruction의 Data 및 Control 흐름
→ PC +4 계산 && PC →instruction Memory
→ control 유닛
(lw)
| ALUOp | Branch | RegDst | MemRead | MemToReg | MemWrite | RegWrite | ALUSrc |
| 00 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
(sw)
| ALUOp | Branch | RegDst | MemRead | MemToReg | MemWrite | RegWrite | ALUSrc |
| 00 | 0 | x | 0 | x | 1 | 0 | 1 |
- ※write back단계에서 레지스터값을 업데이트하지않아 mux가 필요하지않기에 RegDst가 사용되지 않음
- ALUOp : 주소 계산을 위해 add 연산지정
- RegWrite : (1), 메모리에서 읽은 데이터를 레지스터에 저장하기 위함
- ALUSrc : (1), ALU의 두번째 입력으로 immediate값을 선택해야함
→ register File
- Read register1 : rs에서 값 읽기
- Read register 2 : rt 필드는 사용되지않음
→ ALU
- Read data1 : rs
- Read data2 : MUX를 통해 선택된 immediate 값
- ALU = rs주소값 + immediate(3) 메모리 주소계산
→ Data Memory
- 계산된 메모리 주소에서 데이터를 읽어옴
- read Data → MUX(1: data memory의 출력값 / 0: ALU의 연산)
→ Register
📌 Branch-on-Equal Instruction
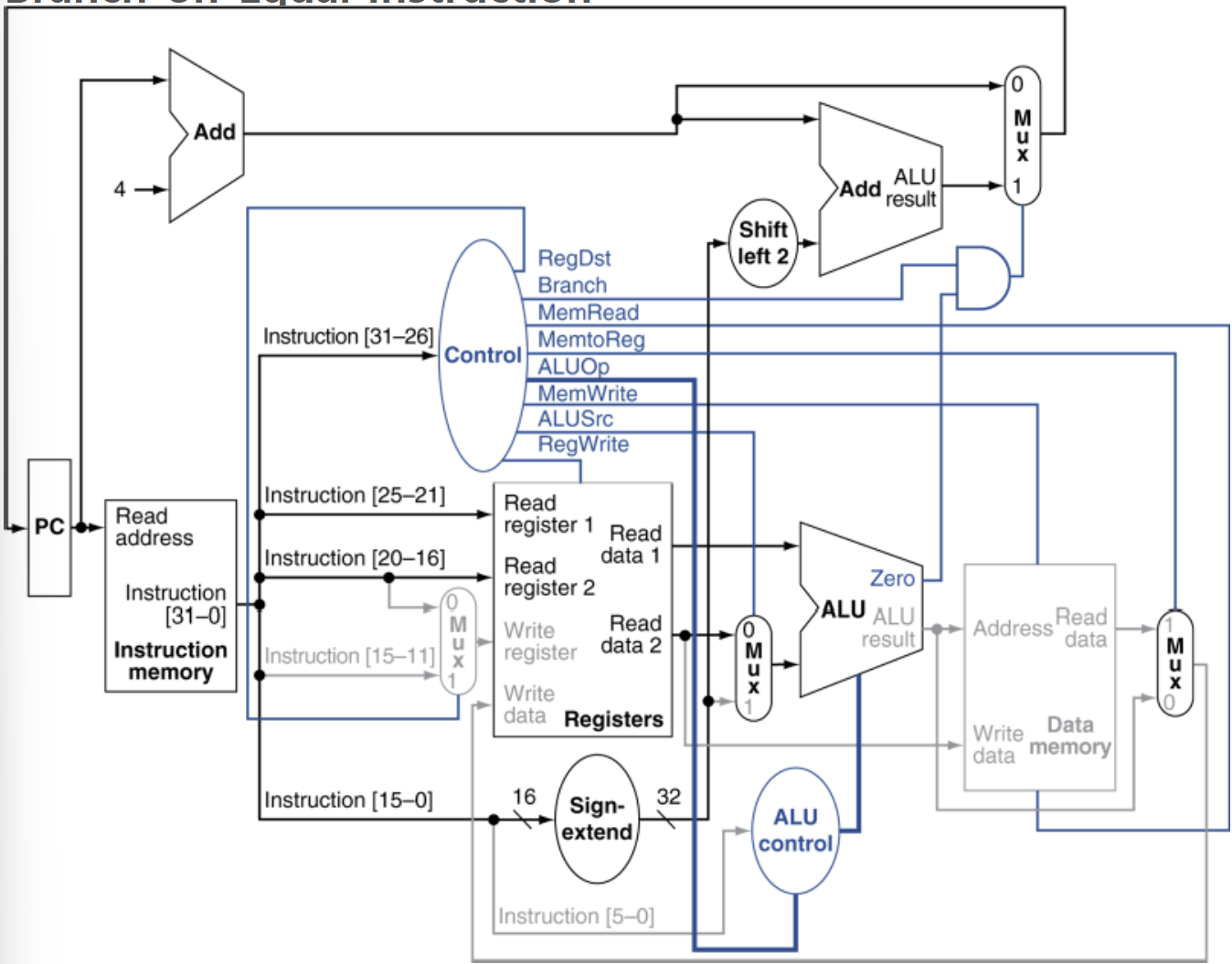
📌 Branch Instruction의 data 및 control흐름
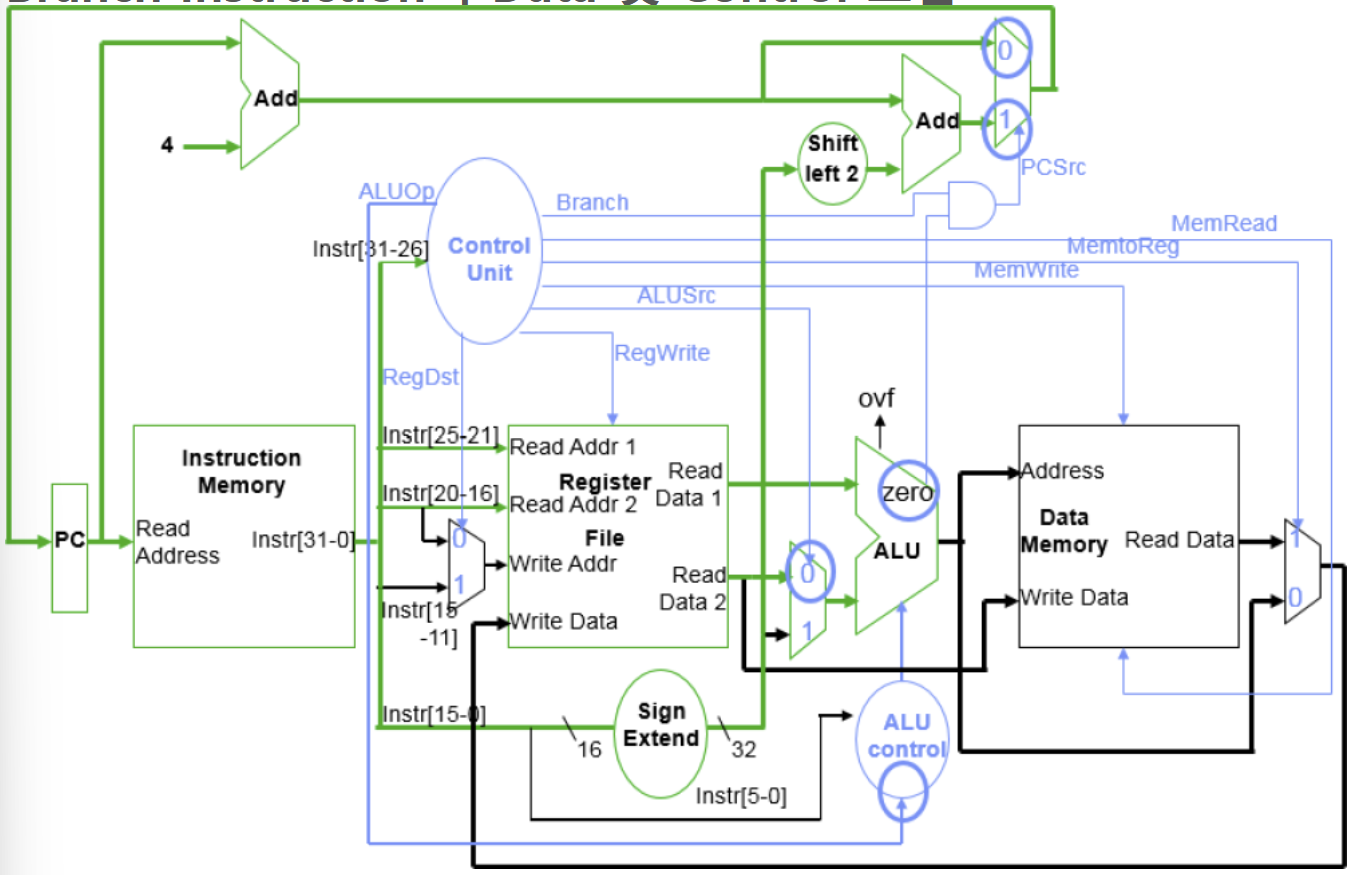
→ PC +4 계산 && PC →instruction Memory
→ control 유닛
| ALUOp | Branch | RegDst | MemRead | MemToReg | MemWrite | RegWrite | ALUSrc |
| 01 | 1 | x | 0 | x | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- ALUOp : 두 레지스터 값 비교를 위해 subtract 연산지정
- RegWrite : 비활성화(0)
- ALUSrc : 비활성화(0), ALU의 두번째 입력은 rt값
→ Sign Extend → Shift left 2 → Add (분기주소계산) → Mux (0:조건거짓일때 다음명령어로, 1:참일때 분기주소로)
→ register File (Read register1 : rs에서 값 읽기, Read register 2 : rt에서 값 읽기)
→ ALU ( Read data1 : rs, Read data2 : rt)
- ALU = rs값 - rt 값
- 결과가 0이면 조건이 참 : 분기
- 결과가 0이 아니면 거짓 , 분기 안하고 다음 명령어로 이동
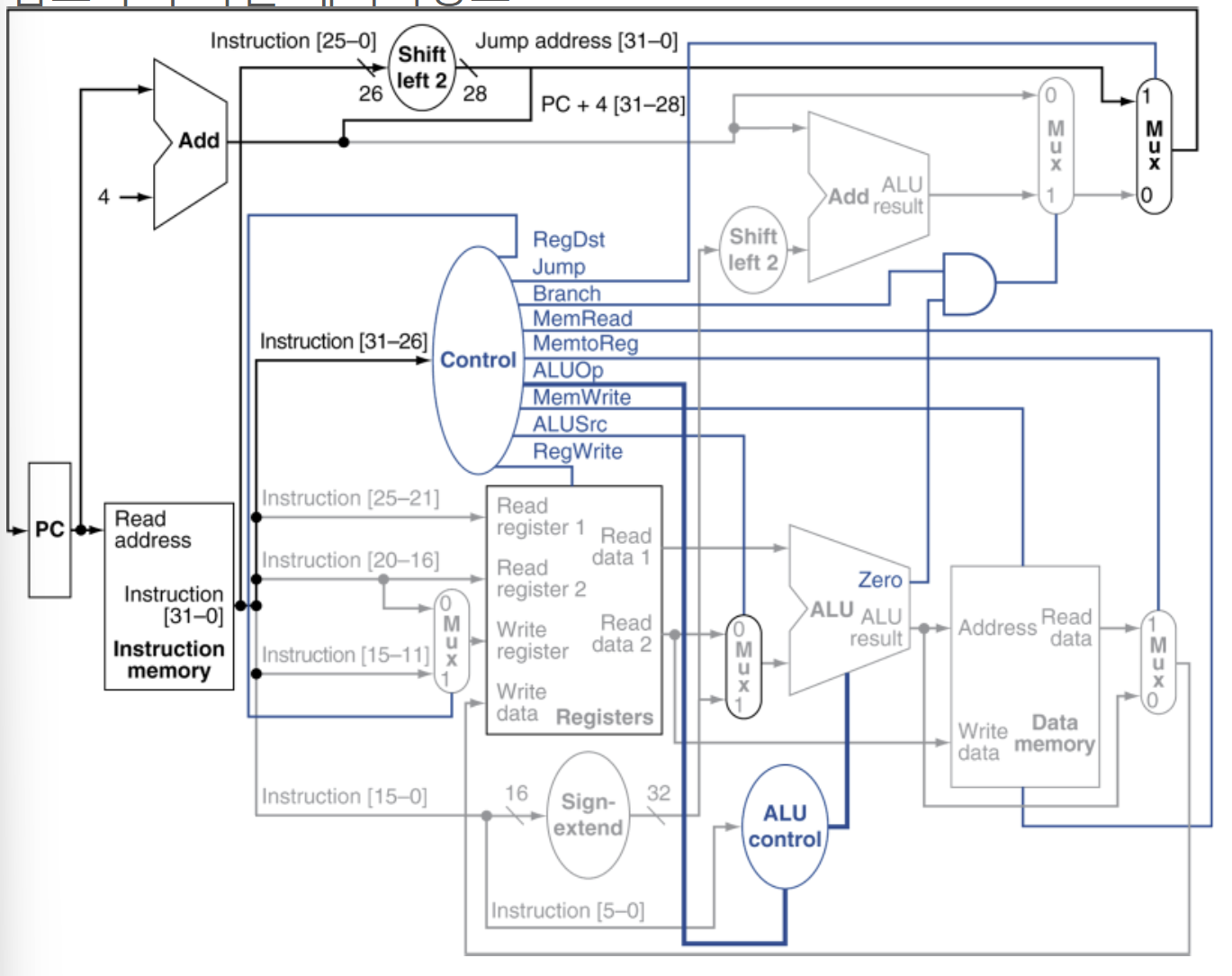
📌Implementing Jumps
| 2 | address |
- word address를 사용한점프 (직접주소를 사용)
- 이어붙이기 방식으로 PC계산
- 26비트의 주소
- 왼쪽으로 shift2번해서 *4의결과
- 현재PC + 상위 4비트를 합침 = 32비트
- opcode로부터 해석된 추가적인 control신호가 필요함
📌 Datapath with jumps added
📌 Adding the Jump Operation
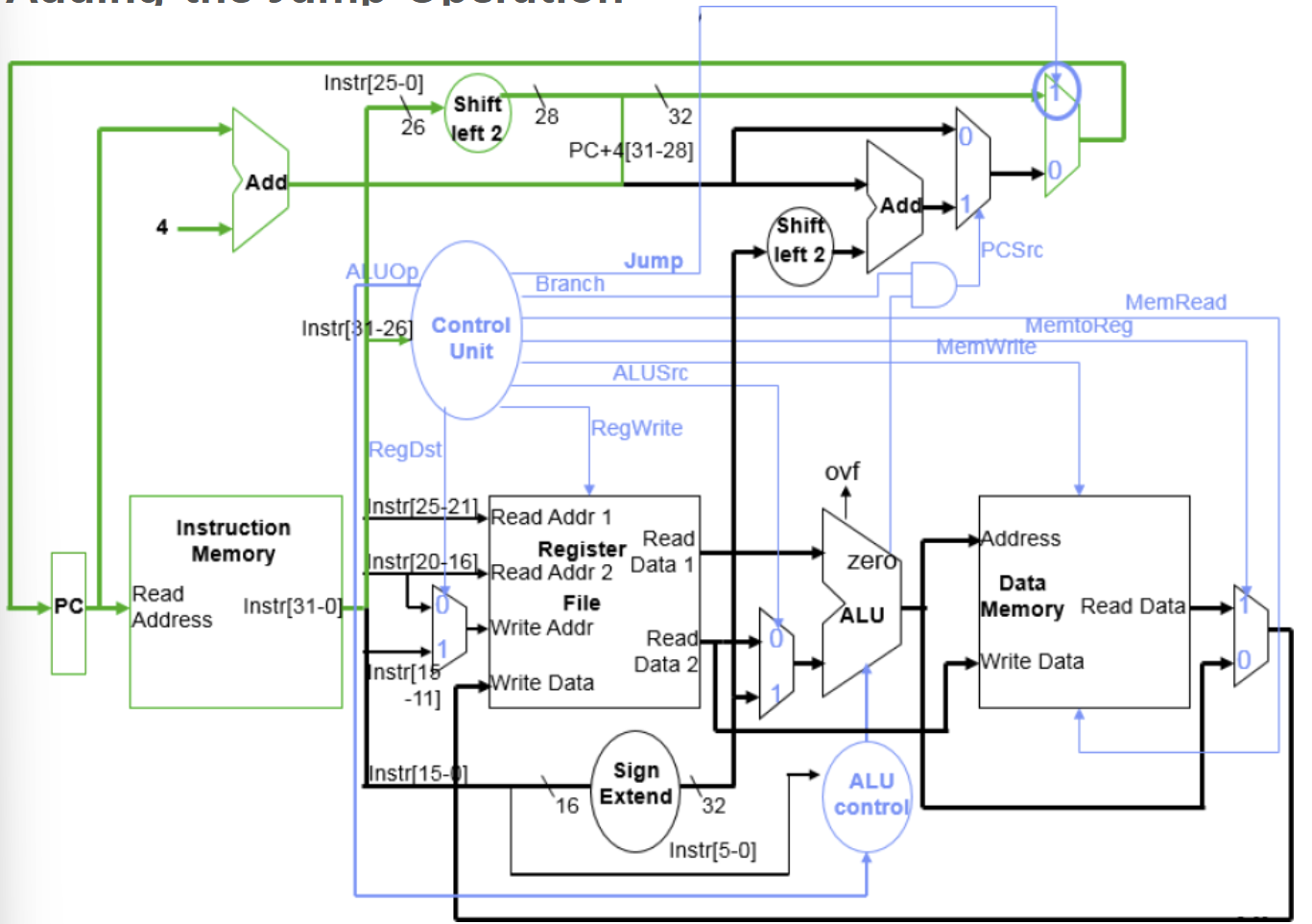
→ PC +4 계산 && PC →instruction Memory
→ control 유닛
| ALUOp | jump | Branch | RegDst | MemRead | MemToReg | MemWrite | RegWrite | ALUSrc |
| x | 1 | 0 | x | 0 | x | 0 | 0 | x |
- ALUOp : (0)
- RegWrite : (0)
- ALUSrc : (0)
- Jump: (1)
→ Shift left 2
→Mux (1 : jump일경우 jump주소로, 0:아닐경우 다음명령어로)
📌 Performance Issues
- 가장 지연시간이 긴 부분이 전체클럭주기를 결정
- 특히 치명적인 경로(경로가 길어 delay가 클 확률이 높은) : load instruction
- instruction memory → register → ALU → data memory → register
- 다른명령어에 다른 주기로 실행 불가
- 모든 명령어는 한 클럭사이클에 실행되어야하며 모두 같은 클럭 사이클 시간이어야함
- 설계 원칙을 위반한다
- 가장 느린것에 맞춰지니까 자주 사용되는 경로를 빠르게 해라에 위배됨
- 자주 사용되는 경로를 빠르게 하려고 해봤자 가장 느린것에 맞춰짐
- 따라서, 파이프라이닝을 통해 성능을 향상시킬 것임
'cs > 컴퓨터구조 및 설계-4장. The Processor' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4.6 Pipelined Datapath and Control (0) | 2024.12.11 |
|---|---|
| 4.5 An Overview of Pipelining (0) | 2024.12.11 |
| 4.3 Building a Datapath (0) | 2024.11.21 |
| 4.2 Logic Design Conventions (0) | 2024.11.21 |
| 4.1 Introduction (0) | 2024.11.20 |





